容器线程安全
可以使用传统的同步容器,如hashTable,也可以使用同步包装器Collecetions.synchronzied*方法,来给原本不同步的容器包装为同步容器;以及通过使用并发包中的线程安全容器类来保证线程安全,如各种并发容器,比如 ConcurrentHashMap、CopyOnWriteArrayList。各种线程安全队列(Queue/Deque),如 ArrayBlockingQueue、SynchronousQueue。
首先HashMap是线程不安全的,其主要体现:
-
在jdk1.7中,在多线程环境下,扩容时会造成环形链或数据丢失。
-
在jdk1.8中,在多线程环境下,会发生数据覆盖的情况。 以下标出可能出问题的代码
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
//并发情况下可能覆盖
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//并发情况下可能覆盖
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//并发情况下可能覆盖
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
//并发情况下可能覆盖
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
get方法的并发问题,无非就是,正在读取过程中,另外一个线程修改了,导致数据与实际不一致;所以主要保证可见性即可;
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
//这里可能出现,该线程可能此时是null,退出,但是与此同时其他线程又初始化了该tab;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
同步包装器Synchronization Wrappers
其实现不过是代理原来的方法,并在每个方法添加上synchronized同步而已
static class SynchronizedList<E>
extends SynchronizedCollection<E>
implements List<E> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7754090372962971524L;
final List<E> list;
SynchronizedList(List<E> list) {
super(list);
this.list = list;
}
SynchronizedList(List<E> list, Object mutex) {
super(list, mutex);
this.list = list;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o)
return true;
synchronized (mutex) {return list.equals(o);}
}
public int hashCode() {
synchronized (mutex) {return list.hashCode();}
}
public E get(int index) {
synchronized (mutex) {return list.get(index);}
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
synchronized (mutex) {return list.set(index, element);}
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
synchronized (mutex) {list.add(index, element);}
}
public E remove(int index) {
synchronized (mutex) {return list.remove(index);}
}
...
}
并发包
基于分离锁实现的 ConcurrentHashMap(1.7)
为什么需要 ConcurrentHashMap?
因为HashTable和同步包装器都它只是使用synchronize进行很粗粒度的同步,性能低,一个线程操作,其他线程都要等待;
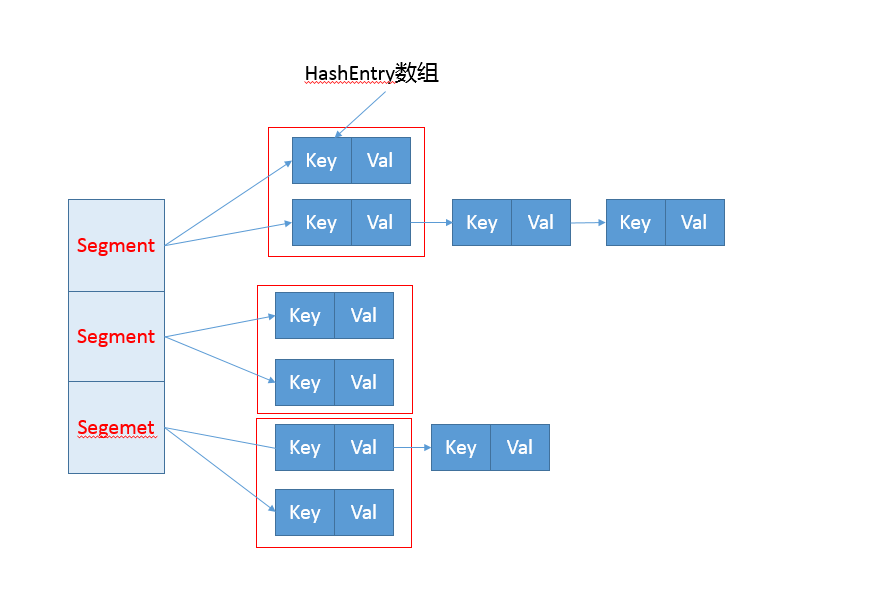
get put的过程
基于上面那张图,我们知道,其实就是多加了一层,使用Segment来分割HashEntry数组,这样我们就可以只锁住部分HashEntry,而不至于锁住所有;
先看基本存储结构Segment;
//继承了ReentrantLock
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
...
/**
* The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table.
*/
final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
...
}
Segment中就由HashEntry组成
/**
* The per-segment table. Elements are accessed via
* entryAt/setEntryAt providing volatile semantics.
*/
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
然后先看put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
简单的说,就说根据hash值获取到对应的Segment,然后在调用Segment中的put;
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
..... //这部分就是在获得锁之后put的过程了,判断是否重复key是否覆盖,不充分将node添加到链表上,判断是否需要扩容
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
这里调用了ReentrantLock的tryLock方法,会尝试去获取当前对象(Segment对象)的锁,如果当前可获取就立即返回true,其他情况返回false;
在scanAndLockForPut,它会不断的尝试去获取锁,当然在尝试的过程中,它还提前做了一些能做的事情,竟然不能put,那它可以先准备好要put的Node,在重试的过程,如果发现要插入的table所在的头结点以被其他线程修改(可能是刚好put在这个点上,也可能是扩容了),那么会在判断是否需要创建Node;
private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
HashEntry<K,V> node = null;
int retries = -1; // negative while locating node
while (!tryLock()) {
HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below
if (retries < 0) {
if (e == null) {
if (node == null) // speculatively create node
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
retries = 0;
}
else if (key.equals(e.key))
retries = 0;
else
e = e.next;
}
else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
lock();
break;
}
else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed
retries = -1;
}
}
return node;
}
总之最后重试达到一定次数后,就会直接lock去获取锁,保证一定能拿到锁,因为前面的操作可能会使它错过获取锁的时机;
ConcurrentHashMap 的 get 方法是非常高效的,因为整个过程都不需要加锁。由于 HashEntry 中的 value 属性是用 volatile关键词修饰的,保证了内存可见性,所以每次获取时都是最新值。
基于CAS + synchronized实现的 ConcurrentHashMap(1.8)
1.7 已经解决了并发问题,并且能支持 N 个 Segment 这么多次数的并发,但依然存在 HashMap 在 1.7 版本中的问题。
那就是查询遍历链表效率太低。
看下1.8中的存储结构图,发现与hashMpa差不多;
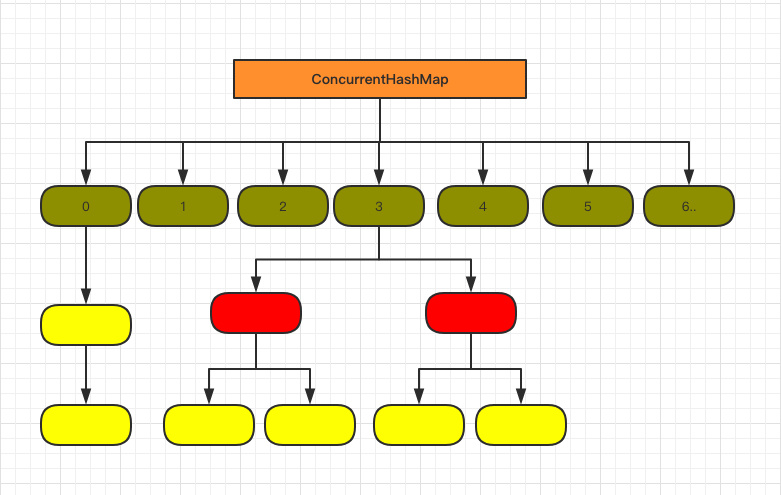
先看具体存储结构,已经没有1.7中的Segment了;
/**
* The array of bins. Lazily initialized upon first insertion.
* Size is always a power of two. Accessed directly by iterators.
*/
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* The next table to use; non-null only while resizing.
*/
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
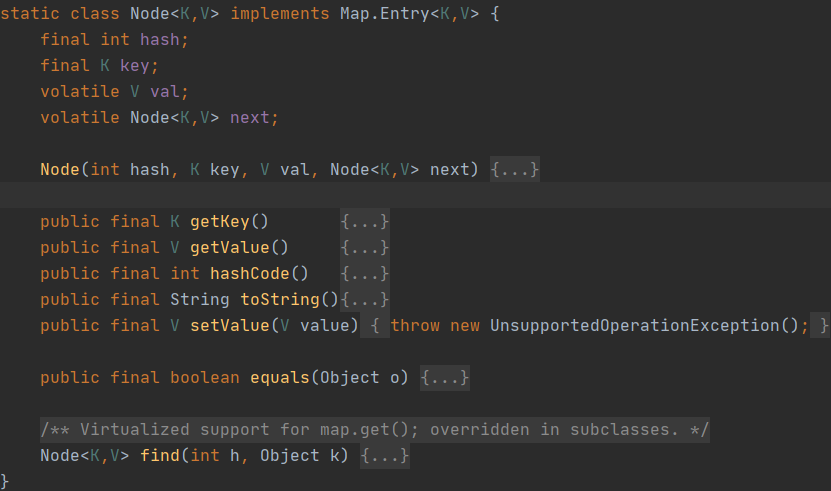 Node中的value和key也同样使用了volatile来保证可见性;
put方法
Node中的value和key也同样使用了volatile来保证可见性;
put方法
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable(); //初始化
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
//当前hash值所在表为空,创建第一个节点利用CAS写入 由于volatile,修改对其他线程可见
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) { //利用 synchronized 锁住这tab[i]的整条链或树
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value; //由于volatile,修改对其他线程可见
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
//由于volatile,修改对其他线程可见
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
get方法就和hashMap的差不多,计算出hashcode值,如果直接就在桶上就直接返回值,如果是红黑树的结构就按红黑树的方式查询返回,否则就是链表的形势查询返回;get全程无锁,通过主要通过volatile来保证并发写对数据修改的可见性;
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
同步迭代和复合操作原子接口
- 内部的Traverser用于迭代容器节点,保证不会抛出ConcuttentModificationException,即可以在迭代的过程中,其他线程对该容器进行添加,删除甚至是扩容操作
- 弱一致性的迭代器可以容忍并发的修改
CocurrentMap提供了一些额外复合操作的原子接口
- 若没有则添加:putIfAbsent()
- 若存在着删除: remove(K key,v value);
- 若相等则替换: replace(K key,V oldValue,V newValue);replave(k key,V newValue);
可参考
详细的源码分析 JDK1.8–深度分析ConcurrentHashMap原理分析
源码注释写的很清楚ConcurrentHashMap 源码解读