Chapter 2. Item 6: Avoid creating unnecessary objects(避免创建不必要的对象)
以下代码每执行一次都会产生一个新的实例对象
String s = new String("volatile"); // DON'T DO THIS!
使用以下代码,可以避免重复创建实例;
String s = "volatile";
使用常量赋值,会在常量池里面创建对象,并会共享这个对象;
String str1 = "volatile";
String str2 = "vo"+"la"+"tile";//这种的编译后会合在一起
System.out.println(str1 == str2);//true
String str3 = "vo"
String str4 = str2+"la"+"tile";//这种也会创建一个新对象;大部分都是这种情况
System.out.println(str1 == str4);//false
使用StringBuilder会创建新的String对象
public String toString() {
// Create a copy, don't share the array
return new String(value, 0, count);
}
其他的基本包装类型也有相似的用法,尽量不要使用new的方式创建包装类型,编译器会自动调用valueOf()方法;
Integer i3 = 1; //编译会自动转换为valueOf()
Integer i4 = 1;
Integer i5 = Integer.valueOf(1);
System.out.println(i3.hashCode());
System.out.println(i4.hashCode());
System.out.println(i3 == i4); //true
System.out.println(i3 == i5); //true
查看valueOf,可以看到Integer缓冲了数值,范围为-128~127;
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
类似的Long、Short、Byted缓存 -128~127 , Char缓存 0~127 都是会调用valueOf()方法;
Double 和 float没有缓存;
Chapter 2.Item 9: Prefer try-with-resources to try-finally(使用 try-with-resources 优于 try-finally)
之所以要有try-with-resources,主要原因就是因为close方法也可以抛出异常;
- 嵌套try-finally
- 异常抑制;try块中抛出的异常会被finally中抛出的异常抑制,也就是外部调用catch到的异常会是finally中抛出的异常;
finally里嵌套try;
public class TestTryWithResources implements Closeable {
private boolean close = false;
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
if (!close) {
System.out.println("Close TestTryWithResources");
close = true;
return;
}
System.out.println("had close ,will throw IOException");
throw new IOException("TestTryWithResources had close");
}
}
public static void testTryCatchSuppressed() throws IOException {
TestTryWithResources testTryWithResources = new TestTryWithResources();
try {
testTryWithResources.close();
throw new IOException("try block throw IOException");
}catch (IOException e){
throw e;
}
finally {
try {
testTryWithResources.close();
}catch (IOException ioException){
throw ioException;
}
}
}
使用try-with-resources
public static void testTryWithResourceSuppressed() throws IOException{
try (TestTryWithResources testTryWithResources = new TestTryWithResources();){
testTryWithResources.close();
throw new IOException("try block throw IOException");
}catch (IOException e){
throw e;
}
}
Close TestTryWithResources
TestTryWithResources had close ,will throw IOException
try block throw IOException
获取被抑制的异常
try {
TestTryWithResources.testTryWithResourceSuppressed();
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
Throwable[] throwables = e.getSuppressed();
Arrays.stream(throwables).sequential().forEach(throwable -> System.out.println(throwable.getMessage()));
}
但是,try-with-resources其实就是语法糖而已,底层还是在原来try-catch-finally;看看反编译的代码
public static void testTryWithResourceSuppressed() throws IOException {
try {
TestTryWithResources var0 = new TestTryWithResources();
Throwable var1 = null;
try {
var0.close();
throw new IOException("try block throw IOException");
} catch (Throwable var10) {
var1 = var10;
throw var10;
} finally {
if (var0 != null) {
if (var1 != null) {
try {
var0.close();
} catch (Throwable var9) {
var1.addSuppressed(var9);
}
} else {
var0.close();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException var12) {
throw var12;
}
}
使用try-with-resources可以将资源声明在try后的括号中,在try块执行结束后自动调用close()接口(前提是这些资源必须实现 AutoCloseable 或者 Closeable接口);
并且块中如果抛出异常,在执行close时也抛出异常,close抛出的异常会被抑制,不过我们仍可以getSuppressed()方法来获取被抑制的异常;其余的与原来的try-catch语句相同;
Chapter 4. Item 17: Minimize mutability(减少可变性)
实例越不可变,越安全易用;比如String,和基本包装类型Integer,Long等等;
- Class由final修饰,表示不可被继承,防止继承的子类对父类进行修改
- 所有字段设为私有,由final修饰;
- 不提供修改内部属性的方法,get返回的不应该是对象本身,而是对象的拷贝,防止泄露被更改;
不可变的好处:
- 天然的并发安全;由于不可变,自然不会存在线程安全问题;
- 使用安全,可以避免被意外修改;作为Map的key值和Set的值都应该时不可变的;
缺点:
- 类似String,由于不可变,所以每次更改其实都是创建了一个新的实例; ```
@Data public final class TestImmutable2 { private String value;
public TestImmutable2(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getValue(){
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value){
this.value = value;
}
public static void testChangeImmutable2(){
Map<TestImmutable2,Integer> changMap = new HashMap<>();
TestImmutable2 t1 = new TestImmutable2("key");
TestImmutable2 t2 = new TestImmutable2("key2");
changMap.put(t1,1);
changMap.put(t2,2);
TestImmutable2 getValue = new TestImmutable2("key");
System.out.printf("isContain:%s,value:%s\n",changMap.containsKey(getValue),changMap.get(getValue));
TestImmutable2 t3 = new TestImmutable2("key3");
changMap.put(t3,3);
t3.setValue("key");
changMap.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.printf("k:%s,v:%s\n",k,v);
});
System.out.printf("t3.value:%s\n",t3.getValue());
TestImmutable2 getValue2 = new TestImmutable2("key3");
System.out.printf("isContain:%s,value:%s",changMap.containsKey(getValue2),changMap.get(getValue2));
} }
isContain:true,value:1 k:TestImmutable2(value=key),v:1 k:TestImmutable2(value=key2),v:2 k:TestImmutable2(value=key),v:3 t3.value:key isContain:false,value:null Process finished with exit code 0
public final class TestImmutable { private final Date startDate; private final Date endDate;
public TestImmutable(Date s,Date e){
this.startDate = s;
this.endDate = e;
}
public Date getStartDate(){
// return new Date(startDate.getTime());
return startDate;
}
public Date getEndDate(){
// return new Date(endDate.getTime());
return endDate;
}
public static void testChangeImmutable(){
Calendar theCa = Calendar. getInstance ();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat( "yyyy-MM-dd" );
theCa.setTime(new Date());
theCa.add(Calendar. DATE, +30);
TestImmutable testImmutable = new TestImmutable(new Date(),theCa.getTime());
System.out.printf("startDate:%s,endDate:%s\n",sdf.format(testImmutable.startDate),sdf.format(testImmutable.getEndDate()));
Calendar theCa2 = Calendar. getInstance ();
theCa2.setTime(new Date());
theCa2.add(Calendar. DATE, +60);
testImmutable.getStartDate().setTime(theCa2.getTimeInMillis());
System.out.printf("startDate:%s,endDate:%s",sdf.format(testImmutable.startDate),sdf.format(testImmutable.getEndDate()));
} } startDate:2021-03-18,endDate:2021-04-17 startDate:2021-05-17,endDate:2021-04-17 ``` 同样的,如果我们将对象作为key,或者Set的值,一旦获取并且更改里面的值,会出现
Chapter 6.Item 36: Use EnumSet instead of bit fields(用 EnumSet 替代位字段)
public class UserRole{
private static final int CHANNEL_MANAGER = 1 << 1; //渠道经理
private static final int CHANNEL_SPECIALIST = 1 << 2; //渠道专员
private static final int CUSTOMER_MANAGER = 1 << 3; //案场助理
....
}
多角色就是 int userRole = CHANNEL_MANAGER & CHANNEL_SPECIALIST;
- 优点: 占用内存小,计算方便,效率高;
- 缺点:不方便转化为字符表达,范围受限;
public enum RoleEnum {
/**
* 渠道经理
*/
CHANNEL_MANAGER(505L, "渠道经理"),
/**
* 渠道专员
*/
CHANNEL_SPECIALIST(509L, "渠道专员"),
/**
* 案场助理
*/
CUSTOMER_MANAGER(508L,"案场助理");
...
}
enum,表示方便,可以附带更多信息。但是计算不方便;
竟然可以附带信息,那么将位域作为enum的属性行不行?可以,提供基本计算接口,但是每次一个enum都得写一遍这种接口;那么抽象一个工具类,利用泛型,提供复用接口;
EnumSet
EnumSet本身就是利用位域来存储enum各个值的并进行相关计算的;
public abstract class EnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* The class of all the elements of this set.
*/
final Class<E> elementType;
/**
* All of the values comprising T. (Cached for performance.)
*/
final Enum<?>[] universe;
...
public static <E extends Enum<E>> EnumSet<E> noneOf(Class<E> elementType) {
Enum<?>[] universe = getUniverse(elementType);
if (universe == null)
throw new ClassCastException(elementType + " not an enum");
if (universe.length <= 64)
return new RegularEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
else
return new JumboEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
}
....
}
class RegularEnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> extends EnumSet<E> {
/**
* Bit vector representation of this set. The 2^k bit indicates the
* presence of universe[k] in this set.
*/
private long elements = 0L;
public boolean add(E e) {
typeCheck(e);
long oldElements = elements;
elements |= (1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal());
return elements != oldElements;
}
public boolean remove(Object e) {
if (e == null)
return false;
Class<?> eClass = e.getClass();
if (eClass != elementType && eClass.getSuperclass() != elementType)
return false;
long oldElements = elements;
elements &= ~(1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal());
return elements != oldElements;
}
public boolean contains(Object e) {
if (e == null)
return false;
Class<?> eClass = e.getClass();
if (eClass != elementType && eClass.getSuperclass() != elementType)
return false;
return (elements & (1L << ((Enum<?>)e).ordinal())) != 0;
}
}
总得来说,EnumSet就是将枚举类型和位域的优点结合起来
Chapter 6. Item 37: Use EnumMap instead of ordinal indexing(使用 EnumMap 替换序数索引)
当我们需要使用Enum作为map的key值时,可以选择用EnumMap,因为EnumMap在内部直接使用数组来进行存储,非常的紧凑和高效;
public class EnumMap<K extends Enum<K>, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V>
implements java.io.Serializable, Cloneable
private transient Object[] vals;
public V get(Object key) {
return (isValidKey(key) ?
unmaskNull(vals[((Enum<?>)key).ordinal()]) : null);
}
}
Map<UserRoleEnum,List<ChannelUserDto>> enumListEnumMap =
channelUserDtoList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(ChannelUserDto::getUserRoleEnum,()-> new EnumMap<>(UserRoleEnum.class), toList()));
Chapter 7. Item 44: Favor the use of standard functional interfaces(优先使用标准函数式接口)
只要标准的函数接口能够满足需求,就不要专门再构建一个新的函数接口;这样会更加容易学习,较少概念内容,提升互操作性优势。
基本的函数式接口就以下6种
| Interface | Function Signature | Example |
|:——-:|:——-:|:——-:|
| UnaryOperator<T> | T apply(T t) | String::toLowerCase |
| BinaryOperator<T> | T apply(T t1, T t2) | BigInteger::add |
| Predicate<T> | boolean test(T t) | Collection::isEmpty |
| Function<T,R> | R apply(T t) | Arrays::asList |
| Supplier<T> | T get() | Instant::now |
| Consumer<T> | void accept(T t) | System.out::println |
其他的接口都是根据这种6种拓展开的;
- Bi*表示有2个参数的变体
- Double表示参数类型位double(supplier返回类型为double),Int,Long同理;
- ToDouble,ToInt,ToLong表示返回值为对应的double,int和long
Chapter 9.Item 61: Prefer primitive types to boxed primitives(基本数据类型优于包装类)
自动拆装箱的bug;
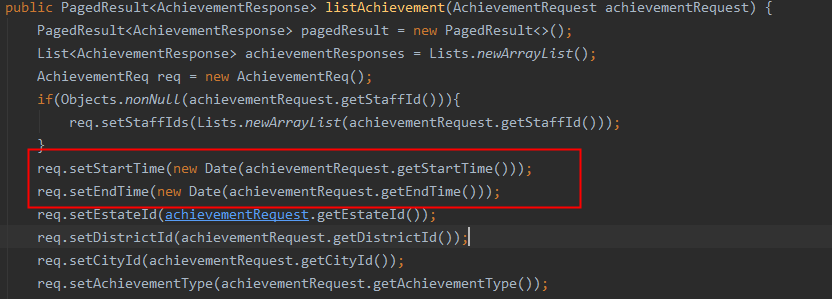 这个地方可能会报npe;
这个地方可能会报npe;
Chapter 12. Item 86: Implement Serializable with great caution(非常谨慎地实现 Serializable)
- 实现 Serializable 接口的一个主要代价是,一旦类的实现被发布,它就会降低更改该类实现的灵活性。我们的dubbo接口参数,一般定义使用之后很少更改,修改字段最保险的方式就是直接新增一个字段;
- 实现 Serializable 接口的第二个代价是,增加了出现 bug 和安全漏洞的可能性;
==反序列化都是一个隐藏构造函数==,如果我们声明一个不允许被构造的类,并且实现了Serializable,指定了serialVersionUID;那么它完全可以借助反序列化一个文件来生成该实例;只要伪造的类拥有同样的serialVersionUID,并且package相同,就可以被反序列化出来;
序列化就是将内存对象转换为能够进行io的数据形式;如json-字符串形式的数据,protobuf,Hessian ,以及java序列化自己的一套序列化方式;
我们目前是利用了jackson进行json序列化的;
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser#BeanSerializer.serialize 方法
往上就是
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind#ObjectWriter.writeValue;
然后就是spring的ResponseBody注解处理中的返回值处理方法;
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation#RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor.handleReturnValue
本质上就是利用反射来进行json字符的序列号的;跟java的Serializable接口没有关系;