将@Autowired注解作用在静态变量上时,不会编译错误,但是当我们调用他时会报NPE异常;
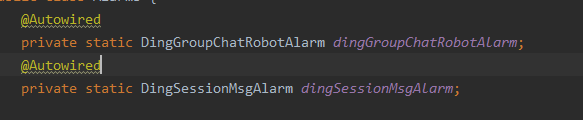
因为类加载后静态变量成员是在内存的共享区,当类在加载静态变量时,spring还上下文还没加载,自然也就无法自动注入;(这一段,似乎不能这么去看) 我们可以用构造函数的方法来实现静态变量的自动注入;当Spring扫描到该注解时,赋值给该静态变量;
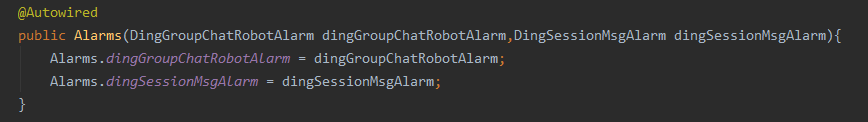 构造方法不需要加Autowired注解的。
如果我的静态属性要设置的是它自己的单例实例,要怎么做呢?
构造方法不需要加Autowired注解的。
如果我的静态属性要设置的是它自己的单例实例,要怎么做呢?
初步猜想
目前来看,bean依赖注入的方式有两种,一种是基于构造函数注入,一种是基于set方法注入;所以在实例化bean的时候,可以调用有参数的构造函数来进行依赖注入,所以不需要@autowired注解也可以;而set方法是在实例化bean后再来调用实现依赖注入;本以为他会自动检测set方法来实现依赖注入,实际上操作之后,没有@Autowired注解的set方法起不到注入的作用,加上注解就成功了,所以猜测在bean实例化之后,再进行依赖注入,此时根据@autowired来寻找需要注入的属性,或者需要调用的set方法;
bean实例化获取候选构造函数
构造函数有以下的可能性
- 默认构造函数(){};
- 带有@Autowired(require = true)或@Autowired(require = false)
- 带有@Require 注解的构造函数
- 有参数的构造函数
会被选入候选构造函数的有
- 在有@Autowired或@Require注解,以及@Autowired(require = false)的构造函数。require的构造函数只能有一个;
- 在仅有@Autowired(require = false)的构造函数下,默认构造函数(){}也会被加入候选构造函数;
- 在没有注解的情况下,如果仅有一个带参数构造函数,那么该函数也会被加入候选构造函数
- 其余情况,不加入;(即只有默认构造函数,或者有多个构造函数)
- (顺便补充,java类不会没有构造函数的,只要定义类,没有声明的话会有默认构造函数,如果主动声明了那就是有,如果访问权限定义为私有,那么这里默认构造会有空,后续会通过反射获得可访问的构造函数来进行构造)
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, final String beanName)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Let's check for lookup methods here...
if (!this.lookupMethodsChecked.contains(beanName)) {
if (AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(beanClass, Lookup.class)) {
try {
Class<?> targetClass = beanClass;
do {
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Lookup lookup = method.getAnnotation(Lookup.class);
if (lookup != null) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
LookupOverride override = new LookupOverride(method, lookup.value());
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = (RootBeanDefinition)
this.beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);
mbd.getMethodOverrides().addOverride(override);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Cannot apply @Lookup to beans without corresponding bean definition");
}
}
});
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Lookup method resolution failed", ex);
}
}
this.lookupMethodsChecked.add(beanName);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
Constructor<?>[] candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
// Fully synchronized resolution now...
synchronized (this.candidateConstructorsCache) {
candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
Constructor<?>[] rawCandidates;
try {
rawCandidates = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +
"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);
}
List<Constructor<?>> candidates = new ArrayList<>(rawCandidates.length);
Constructor<?> requiredConstructor = null;
Constructor<?> defaultConstructor = null;
Constructor<?> primaryConstructor = BeanUtils.findPrimaryConstructor(beanClass);
int nonSyntheticConstructors = 0;
for (Constructor<?> candidate : rawCandidates) {
if (!candidate.isSynthetic()) {
nonSyntheticConstructors++;
}
else if (primaryConstructor != null) {
continue;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(candidate);
if (ann == null) {
Class<?> userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanClass);
if (userClass != beanClass) {
try {
Constructor<?> superCtor =
userClass.getDeclaredConstructor(candidate.getParameterTypes());
ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(superCtor);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// Simply proceed, no equivalent superclass constructor found...
}
}
}
if (ann != null) {
if (requiredConstructor != null) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructor: " + candidate +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation already: " +
requiredConstructor);
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
if (required) {
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Invalid autowire-marked constructors: " + candidates +
". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation: " +
candidate);
}
requiredConstructor = candidate;
}
candidates.add(candidate);
}
else if (candidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {
defaultConstructor = candidate;
}
}
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
// Add default constructor to list of optional constructors, as fallback.
if (requiredConstructor == null) {
if (defaultConstructor != null) {
candidates.add(defaultConstructor);
}
else if (candidates.size() == 1 && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Inconsistent constructor declaration on bean with name '" + beanName +
"': single autowire-marked constructor flagged as optional - " +
"this constructor is effectively required since there is no " +
"default constructor to fall back to: " + candidates.get(0));
}
}
candidateConstructors = candidates.toArray(new Constructor<?>[0]);
}
else if (rawCandidates.length == 1 && rawCandidates[0].getParameterCount() > 0) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {rawCandidates[0]};
}
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 2 && primaryConstructor != null &&
defaultConstructor != null && !primaryConstructor.equals(defaultConstructor)) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor, defaultConstructor};
}
else if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 1 && primaryConstructor != null) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor};
}
else {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[0];
}
this.candidateConstructorsCache.put(beanClass, candidateConstructors);
}
}
}
return (candidateConstructors.length > 0 ? candidateConstructors : null);
}
ConstructorResolver
public BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd,
@Nullable Constructor<?>[] chosenCtors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
BeanWrapperImpl bw = new BeanWrapperImpl();
this.beanFactory.initBeanWrapper(bw);
Constructor<?> constructorToUse = null;
ArgumentsHolder argsHolderToUse = null;
Object[] argsToUse = null;//构造函数参数
.......
int minNrOfArgs;
if (explicitArgs != null) {
minNrOfArgs = explicitArgs.length;
}
else {
ConstructorArgumentValues cargs = mbd.getConstructorArgumentValues();
resolvedValues = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
minNrOfArgs = resolveConstructorArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, cargs, resolvedValues);
}
for (Constructor<?> candidate : candidates) {
int parameterCount = candidate.getParameterCount();
if (constructorToUse != null && argsToUse != null && argsToUse.length > parameterCount) {
// Already found greedy constructor that can be satisfied ->
// do not look any further, there are only less greedy constructors left.
break;
}
if (parameterCount < minNrOfArgs) {
continue;
}
//获得构造函数所需要的参数
ArgumentsHolder argsHolder;
Class<?>[] paramTypes = candidate.getParameterTypes();
if (resolvedValues != null) {
try {
String[] paramNames = ConstructorPropertiesChecker.evaluate(candidate, parameterCount);
if (paramNames == null) {
ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd = this.beanFactory.getParameterNameDiscoverer();
if (pnd != null) {
paramNames = pnd.getParameterNames(candidate);
}
}
//获得关键的argsHolder
argsHolder = createArgumentArray(beanName, mbd, resolvedValues, bw, paramTypes, paramNames,
getUserDeclaredConstructor(candidate), autowiring, candidates.length == 1);
}
catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Ignoring constructor [" + candidate + "] of bean '" + beanName + "': " + ex);
}
// Swallow and try next constructor.
if (causes == null) {
causes = new LinkedList<>();
}
causes.add(ex);
continue;
}
}
else {
// Explicit arguments given -> arguments length must match exactly.
if (parameterCount != explicitArgs.length) {
continue;
}
//如果已经有了直接拿来构造
argsHolder = new ArgumentsHolder(explicitArgs);
}
int typeDiffWeight = (mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() ?
argsHolder.getTypeDifferenceWeight(paramTypes) : argsHolder.getAssignabilityWeight(paramTypes));
// Choose this constructor if it represents the closest match.
if (typeDiffWeight < minTypeDiffWeight) {
constructorToUse = candidate;
argsHolderToUse = argsHolder;
argsToUse = argsHolder.arguments;//在这里提取出参数
minTypeDiffWeight = typeDiffWeight;
ambiguousConstructors = null;
}
....
}
Assert.state(argsToUse != null, "Unresolved constructor arguments");
//最终构造
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, constructorToUse, argsToUse));
return bw;
}
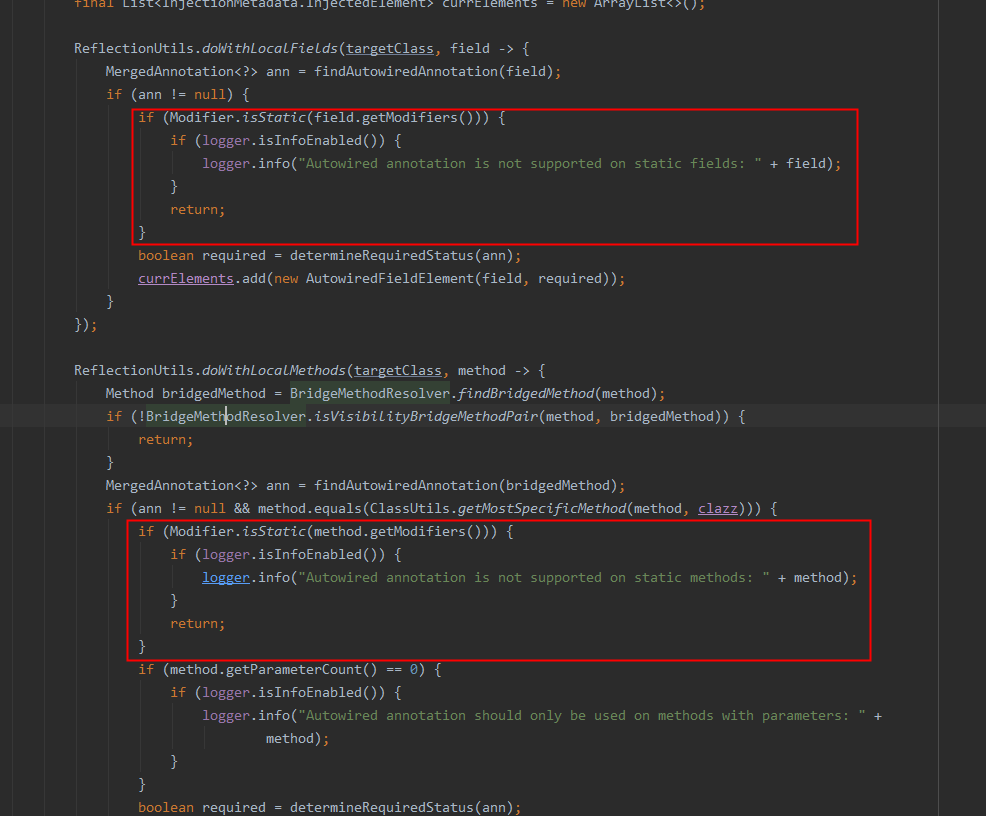
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//寻找所有Autowired注解file
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
//寻找所有Autowired注解method
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
InjectionMetadata
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)
throws Throwable {
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
else {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
try {
Method method = (Method) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
spring不建议自动注入静态变量和使用静态方法来注入
依赖注入的主要目的,是让容器去产生一个对象的实例然后管理它的生命周期,然后在生命周期中使用他们,这会让单元测试工作更加容易。而如果你使用静态变量/类变量就扩大了使用范围,使得不可控了。这种static field是隐含共享的,并且是一种global全局状态,Spring并不推荐你去这么做
这里的概念问题是注释驱动的注入发生在每个bean实例上。我们不应该在这里注入静态字段或静态方法因为那将发生在该类的每个实例中。注入生命周期与实例生命周期绑定,而不是与类生命周期绑定。实例状态和静态访问器之间的桥接(如果确实需要的话)取决于具体bean实现,但可以说框架本身不应该这样做。
扫描时忽略了static变量和方法;
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
...
do {
...
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
...
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
...
}
});
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
...
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
...
}
});
...
}
...
}
这里确实不是这个原因,及时是静态变量,在扫描该类所有带有注解的属性并注入依赖按理来说是没有问题的,原因就在于spring不推荐给静态变量和方法进行依赖注入,代码里也是直接就忽略了。
@Inject、@Autowired、@Resource、@Qualifier
@Inject
@Named(value = "ddgc")
public void setDingGroupChatRobotAlarm(DingGroupChatRobotAlarm dingGroupChatRobotAlarm){
Alarms.dingGroupChatRobotAlarm = dingGroupChatRobotAlarm;
}
@Resource(name = "ddgc")
public void setDingGroupChatRobotAlarm(DingGroupChatRobotAlarm dingGroupChatRobotAlarm){
Alarms.dingGroupChatRobotAlarm = dingGroupChatRobotAlarm;
}
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "ddggc") //@Named也可以
public void setDingGroupChatRobotAlarm(DingGroupChatRobotAlarm dingGroupChatRobotAlarm){
Alarms.dingGroupChatRobotAlarm = dingGroupChatRobotAlarm;
}
从上面可以看出他们之间的使用区别,总的来说不大,都可以实现依赖注入,这里因为都是方法的例子,但其实@Quilfier可以单独作用在变量和参数上,不能单独作用在方法上,不过可以和Autowired配合,类似Named; @Resource是JSR250的实现,比较旧了,@Inject 则是JSR330规范的实现;
参考
想用@Autowired注入static静态成员?官方不推荐你却还偏要这么做