EnableAsync注解注释说明
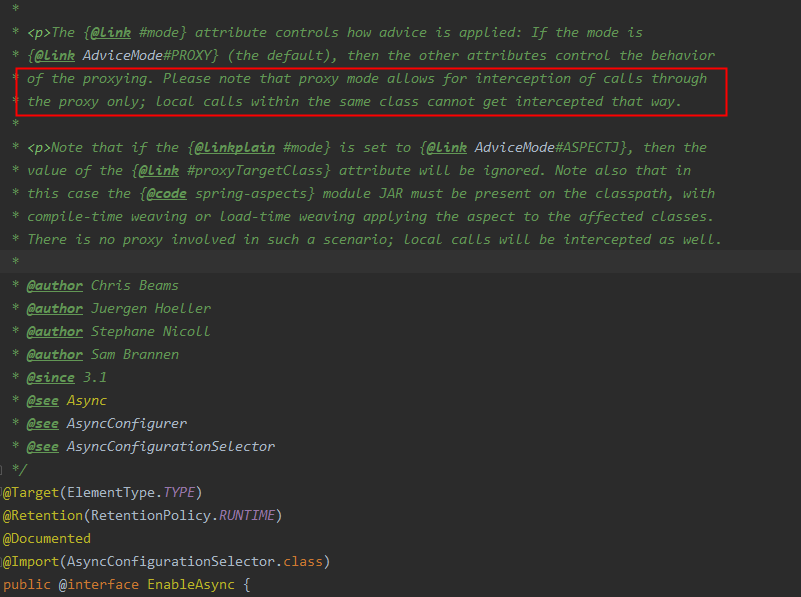
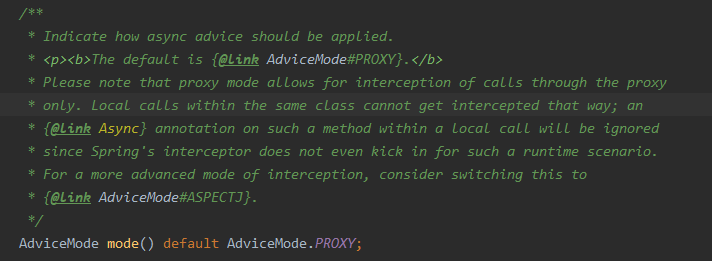
从上面这两段话知道 AdviceMode指出应该如何应用异步操作;默认方式为 AdviceMode.PROXY;这种方式只允许通过代理去截取调用,而同个类中的本地调用方式是不会被拦截的;
原因
spring 使用动态代理实现aop功能,而实现动态代理的手段有两种,一种是jdk动态代理,一种是CGLib代理;
jdk动态代理
jdk动态代理要求 被代理类必须==实现接口==,因为jdk代理需要获取该接口的Class和加载器信息,以及代理处理逻辑(实现InvocationHandler.invoke),来对该接口所有方法进行代理,代理到invoke方法上,并返回该代理对象并向上转型为该接口;所以该类如果有非接口上的方法,那么这些方法是无法被代理的,并且如果该类无接口实现,它就无法应用jdk动态代理来生成代理对象;
而生成的代理类,是Proxy类的子类;
CGLib动态代理
CGLib是利用ASM字节码生成框架,直接对需要代理的字节码进行操作,生成该类的一个子类,并重写了类的所有可以重写的方法,在重写的过程中,将我们定义的额外逻辑写入到方法中;
这里测试下visitBiz,afterVisitAsyncUpdateData这两个没有实现接口的类
String afterVisitSuperClass = afterVisitAsyncUpdateData.getClass().getSuperclass().getName();
String afterVisitClass = afterVisitAsyncUpdateData.getClass().getName();
String thisClass = this.getClass().getName();
String thisSuperClass = this.getClass().getSuperclass().getName();
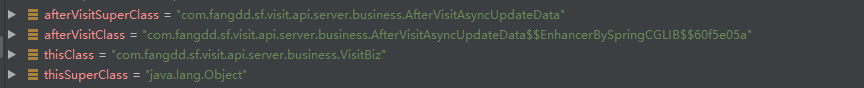
可以看到,他用的是CGLib代理,而这里调用外部类对象的时候,用的是代理,但是如果在同类中调用本类的方法,用的是原本的实例对象,而不是代理,所以这里就已经能够解释为什么在本地类中使用@Async注解的方法无法起到异步了,因为他根本就没调用代理类的代理方法,而是直接调用的原方法;
而由于代理的方法是继承原类,所以也能解释为什么@Async无法注解到private类上,因为这样这个方法就无法给代理(重写)
总结
@Async默认情况下使用代理默认来运行拦截器,所以当我们需要使用异步方法时,需要调用的是代理对象上的方法,而不是原对象的方法,否则不走代理当然也就无法异步;而我们在本地类中去调用注解了@Async方法时,实际上就是调用的原对象方法,而调用其他类的方法时,由于有@Autowrite,获取到该Bean为代理Bean,调用的就是代理对象的方法;
直接在本类中调用@Async注解过的方法,调用的方式是this.@Async-after();也就是我们获取的是原类的对象,而不是代理对象,而通过@AutoWrite方式注入进来的对象,也就是Bean对象,就会将其代理对象注入进来,这样调用的就是代理对象的方法;
拓展
然后就是关于这个代理的生成,Spring在启动时会扫描所有的Class文件,有相关的注解的Class会构造Bean,而这里的由于有@Async注解,会构造为代理Bean;
//AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
....
if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) { //检查是否含有注解
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(bean);
// Copy our properties (proxyTargetClass etc) inherited from ProxyConfig.
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
return proxyFactory.getProxy(this.beanClassLoader);
}
// No async proxy needed.
return bean;
}
advisor就是aop处理器,也是CBGLIC动态代理的拦截器或者JDK代理里的HandlerInvocation;而这里是异步操作,所以会需要用到executor来生成;如下代码;
//public class AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryAware {
...
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
//这里生成advisor;
AsyncAnnotationAdvisor advisor = (this.executor != null ?
new AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(this.executor) : new AsyncAnnotationAdvisor());
....
this.advisor = advisor;
}
...
}
AsyncAnnotationAdvisor类的代码
public class AsyncAnnotationAdvisor extends AbstractPointcutAdvisor implements BeanFactoryAware {
...
public AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(Executor executor) {
...
this.advice = buildAdvice(executor);
...
}
protected Advice buildAdvice(Executor executor) {
return new AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor(executor);
}
}
AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor类,继承AsyncExecutionInterceptor
public class AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor extends AsyncExecutionInterceptor {
public AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor(Executor defaultExecutor) {
super(defaultExecutor);
}
}
继续看AsyncExecutionInterceptor类;它继承AsyncExecutionAspectSupport,实现MethodInterceptor接口,而这个接口就是到时候代理类方法里调用的入口了,通过MethodInvocation来调用原方法;而这里的defaultExecutor,会有默认的异步池,如果有的话,就会是我们自己构建的异步线程池;
public class AsyncExecutionInterceptor extends AsyncExecutionAspectSupport
implements MethodInterceptor, Ordered {
...
public AsyncExecutionInterceptor(Executor defaultExecutor) {
super(defaultExecutor);
}
...
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
specificMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
AsyncTaskExecutor executor = determineAsyncExecutor(specificMethod);
if (executor == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No executor specified and no default executor set on AsyncExecutionInterceptor either");
}
Future<?> result = executor.submit(
new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
try {
Object result = invocation.proceed();
if (result instanceof Future) {
return ((Future<?>) result).get();
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
ReflectionUtils.rethrowException(ex);
}
return null;
}
});
if (Future.class.isAssignableFrom(invocation.getMethod().getReturnType())) {
return result;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
}